

As a result of the electronegativity the hydrogen atom will have a partial positive charge and will therefore be electrostatically attracted to the lone pair of electrons on one of these electronegative atoms on a nearby molecule. To form a hydrogen bond we need molecules which contain a hydrogen atom which is bonded to one of the most electronegative elements (N, O or F). Hydrogen bonds are the strongest kind of intermolecular force, but are still much weaker than the covalent bonds that hold the atoms together inside a molecule - remember the intermolecular forces operate from one molecule to another. Hydrogen bonds are not really bonds but intermolecular forces - weak forces which arise between molecules. It is also a linear molecule (O=O) which makes it non-polar and insoluble in water. NOTE: Possibly confusing is a molecule like #O_2#, which has no bonds between O and H, but rather just a double bond between the two atoms of oxygen.

The solubility of carbon dioxide is increased when the water is cold, and decreased greatly when the water is warm. This means that carbon dioxide is less soluble in water than polar molecules are. #CO_2# can form hydrogen bonds with water, but its linear shape makes it a nonpolar molecule. The polarity of these molecules indicates that they will dissolve in water. Some examples of polar molecules which can hydrogen bond are ammonia ( #NH_3#) and methanol ( #CH_3OH#). This means the molecules will be soluble in a polar solvent such as water. The presence of hydrogen bonding between molecules of a substance indicates that the molecules are polar. Molecules which are capable of hydrogen bonds have hydrogen atoms which are covalently bonded to highly electronegative elements (O, N, F). In summary, hydrogen bonds are (relatively weak) intermolecular forces, while covalent and ionic bonds are (relatively strong) intramolecular forces. Hydrogen bonds have strengths ranging from 5 kJ/mol to 50 kJ/mol.
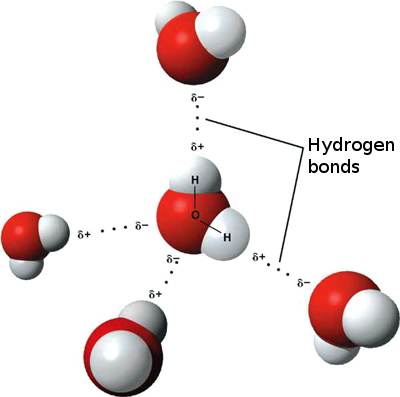
Water is the best-known compound that has hydrogen bonds. They exist when you have a negative #"O"#, #"N"#, or #"F"# atom in one molecule and a positive #"H"# atom attached to an #"O"#, #"N"#, or #"F"# atom in another molecule. Hydrogen bonds are especially strong intermolecular forces. The covalent bonds are intramolecular bonds because they hold the atoms together in a single molecule.Ĭovalent bond strengths range from 100 kJ/mol to 1100 kJ/mol. Ionic bond strengths (lattice energies) range from 600 kJ/mol to 6000 kJ/mol.Ĭovalent bonds form when two atoms share electrons. Ionic bonds are intramolecular bonds, because the ions exert forces among the ions of the same compound. The ions in ionic solids are close to each other, so ionic attractions are strong. The electrostatic attraction between these ions is an ionic bond. The atom that gains an electron becomes a negative ion. The atom that loses an electron becomes a positive ion. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers electrons to another atom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
